Goodwill is a long-term (or noncurrent) asset categorized as an intangible asset. The amount of goodwill is the cost to purchase the business minus the fair market value of the tangible assets, the intangible assets that can be identified, and the liabilities obtained in the purchase. This is the period of time that it will be economically feasible to use an asset. Useful life is used in computing depreciation on an asset, instead of using the physical life. For example, a computer might physically last for 100 years; however, the computer might be useful for only three years due to technology enhancements that are occurring. As a consequence, for financial statement purposes the computer will be depreciated over three years.

Contra assets

Instead of changing the main asset account, reductions are tracked separately. Common contra asset accounts include accumulated depreciation, allowance for doubtful accounts, and accumulated amortization. A contra account is an account used to reduce the value of a related account on your books. For example, most asset accounts have debit balances, while their contra accounts—such as accumulated depreciation—carry credit balances. A contra asset account normally holds a credit balance as it is meant to reduce the debit balance of its corresponding asset.
- CCC bought equipment and machinery worth $100,000 at the beginning of the current financial year and estimates that the equipment and machinery will depreciate by $10,000 every year.
- Try an interactive demo to see how Ramp can help you streamline your financial reporting.
- Of that amount, it is estimated that 1% of that amount will become bad debt at some point in the future.
- A contra revenue account’s typical balance is debit because the normal revenue account has a credit balance.
- Wages Payable is a liability account that reports the amounts owed to employees as of the balance sheet date.
- Accurate records prevent overstatement of assets and revenues, thereby aiding in sound decision-making; imagine knowing exactly how much those accounts receivable are truly worth, beyond optimistic estimations.
- The credit balance in this account comes from the entry wherein Bad Debts Expense is debited.
Contra Accounts: Explained, Popular Types and Examples
- While sales returns adjust revenue, some businesses also need to factor in discounts on financial instruments like notes receivable.
- By stating this information separately in a contra asset account, a user of financial information can see the extent to which a paired asset should be reduced.
- By recording the offset in a separate contra account, accountants can see how much of the value in the main account has been offset.
- At the end of the accounting year, the ending balances in the balance sheet accounts (assets and liabilities) will carry forward to the next accounting year.
- The most prominent of these include allowing companies to present a more accurate picture of their assets.
The accumulated depreciation account appears on the balance sheet and reduces the gross amount of fixed assets. The natural balance in a contra asset account is a credit balance, as opposed to the natural debit balance in all other asset accounts. There is no reason for there to ever be a debit balance in a contra Mental Health Billing asset account; thus, a debit balance probably indicates an incorrect accounting entry.
Common mistakes to avoid with contra accounts
- Another type of contra account is known as “contra revenue,” which is used to adjust gross revenue to calculate net revenue, i.e. the “final” revenue figure listed on the income statement.
- Explore the purpose and types of contra accounts in financial statements, enhancing clarity and accuracy in financial reporting.
- A company creates allowances for doubtful accounts to record the portion of accounts receivable which it believes it will no longer be able to collect.
- The company estimates that it will not be able to collect 1,000 from its customers.
- Contra accounts are used to help a company report the original amount of a transaction as well as reductions that may have happened.
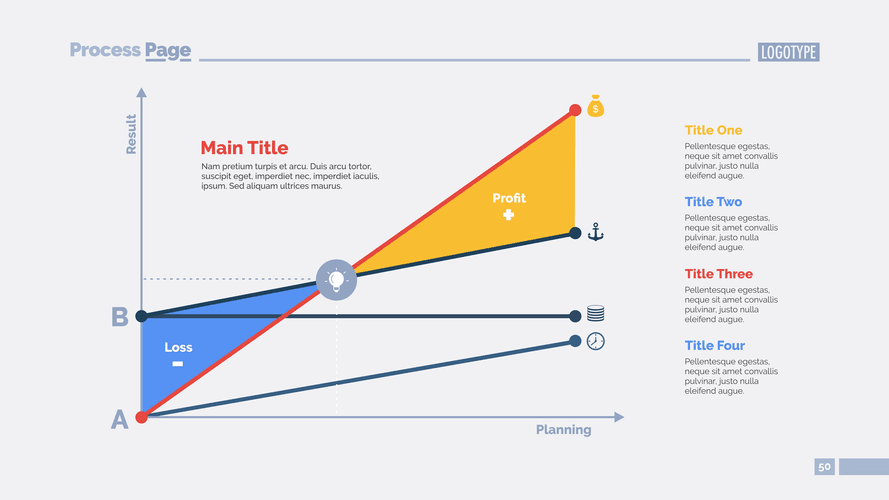
The total amount of the stockholders’ equity section is the difference between the reported amount of assets and the reported amount of liabilities. Similar to liabilities, stockholders’ equity can be thought of as claims to (and sources of) the corporation’s assets. The amount results from the timing of when the depreciation expense is reported.
Contra Revenues and Expenses
A high level of financial leverage may be viewed by lenders as a high level of risk. The final liability appearing on a company’s balance sheet is commitments and https://marickhensmusic.be/the-fifo-method-for-cost-of-goods-sold/ contingencies along with a reference to the notes to the financial statements. Given the above information, the company’s December 31 balance sheet will report $1,500 as the current asset prepaid expenses. On February 28 prepaid expenses will report $900 (3 months of the insurance cost that is unexpired/still prepaid X $300 per month), and so on.
Avoiding Adjusting Entries
A contra account is a general ledger account contra-asset account with a balance that is the opposite of another, related account that it is paired with. A contra account is an account listed within a general ledger with the purpose of capturing the reduced value of a paired or related account when the two are added together. Whether reported as separate lines on the financial report or as a cumulative value, the net amount of the pair of accounts is called the “net book value” of the individual asset.